Home > Information > News
#News ·2025-01-03
As an overseas Internet finance platform, Akulaku uses large models to optimize scenarios such as financial risk control, customer service and e-commerce recommendation, and enhances risk control system efficiency and user experience by integrating images (such as KYC face recognition), text (such as intelligent customer service) and equipment data. The introduction of large models aims to increase efficiency and reduce the burden on business personnel by optimizing small model construction and workflow automation. The application of agents in the financial field includes fraud investigation and data analysis assistants, which indicates the possibility of constructing AGI-like systems with the aid of large models, which can further improve the efficiency and effect of financial risk control, and has a wide range of application prospects in the financial field. This article will share Akulaku's large model implementation practice in the field of financial risk control.
First, a brief introduction of the company's business background.
Akulaku is an Internet financial service provider focusing on overseas markets, including online shopping and installment payment, cash loans, insurance, etc., mainly used in financial risk control, e-commerce intelligent customer service and e-commerce recommendation scenarios. Whether in user audit, credit assessment, or anti-fraud identification and other links, simple manual operation and business rule judgment can not efficiently and accurately deal with a large number of user requests, and intercept various black attacks. Therefore, our overall goal is to build an agile and efficient intelligent risk control system based on various technical means to cope with various threats and continuously improve the user experience.
Specific application scenarios include credit application, login verification, order verification, collection, customer service return visit and other business links, which will involve different modes of data:

Even before the rise of Big models, we continued to provide a variety of AI models to the business, covering the various modal data described earlier. With the emergence of large models, we want to further improve the effectiveness of intelligent risk control systems across all business lines and data forms. The overall vision is to build an agent system. The big model brings us one step closer to AGI general artificial intelligence, and we're trying to build an AGI for finance. An agent system mainly consists of the following three important modules [1] :
Knowledge including various business decisions is usually fixed in the definition of the chain of agents, that is, a chain in LangChain. The system as a whole is a combination of various agents.
Various data and metadata in a business system may be stored in one or more external databases.
Business models and business logic of various proprietary fields, including various image models, NLP models, discriminant models of risk control, and some specific business logic of risk control systems, etc.

The agent system and our existing systems, including risk control system and model system, are not a newly generated system separated from each other, but evolved from the original system. Specific landing is divided into two categories:
The first category is enhancements to tools. For example, for a specific image model in the KYC module, optimize its performance. You can use the ability of the large model to understand the instructions, and the general knowledge and generalization ability of the corresponding language it carries, to do data enhancement and guidance, to enhance the proprietary model of a specific link. This is enhancements to tools.
The second Angle is to strengthen planning and memory. The object of the second direction is human. We hope to extract the business knowledge and decisions involved in the existing tedious repetitive work of business students, fix them in a chain of agents, and build corresponding agent roles. After the concept of the agent and the large model is proposed, when we do the requirements, although the specific landing is still implemented one by one, before landing, we will think about the relationship between these needs, not in the perspective of a single scene or a single model, but in the perspective of a role to think. For example, what we need to do now is optimize the role of data analyst, or optimize the role of fraud investigator.
Here are some examples to illustrate how we achieved the big model landing.
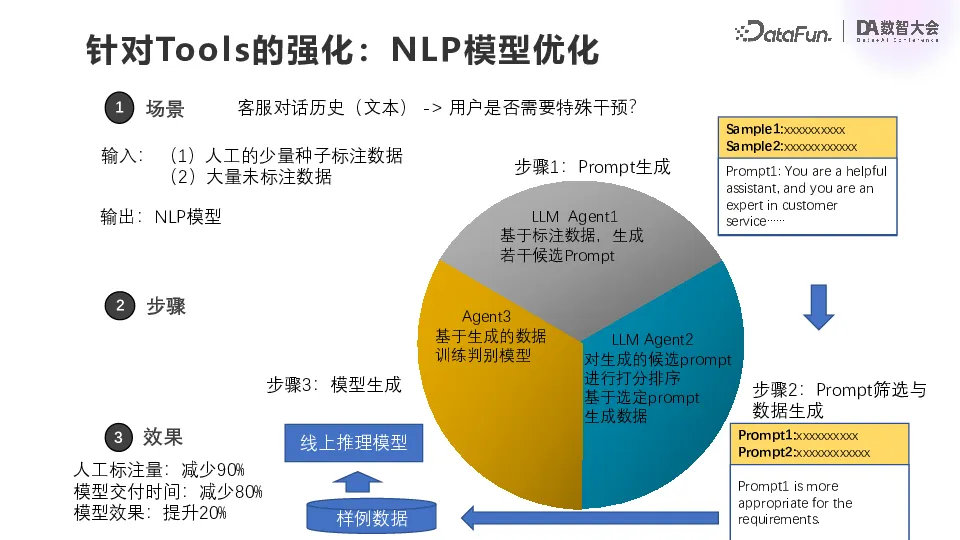
First, for tools enhancement, the first example is a scenario from a digital financial system that determines whether a user needs special intervention based on customer service conversation history. Traditionally, faced with this problem, the model team first needed to accumulate or annotate the data, so the entire delivery and iteration process would be lengthy and inefficient.
After the introduction of the large model, there is no longer a need for 100,000 samples, only a small amount of manually labeled data, probably several hundred to about 1000. Firstly, a large model Agent generates candidate prompt words based on annotated data, which is what I hope the sample data should look like. Then the second Agent will sort and score the aforementioned Agent, select a good prompt and send it to the large model to generate data. The characteristic of the large model is that it can generalize, but it is relatively slow, and slow is not too big a problem here, because the amount of training data it requires is only 100,000 levels, not particularly much, based on such sample data you can do an online reasoning model.
Some of you might ask why not just put this big model online? The main reason is that the daily throughput requirements of the current system are very high, and if you want to achieve very fast responses in large models, it is difficult to avoid latency. Therefore, a better approach is to directly let it generate data, distillation data, and then generate small models to iterate the corresponding modules of the business system.
The result was a significant reduction in manual labeling of this requirement by 90%, a significant reduction in model delivery time, and a 20% improvement in model effectiveness. What is most satisfying to the business is the reduction in the amount of annotations and delivery time, which means that the overall system is more agile and more efficient in responding to change.
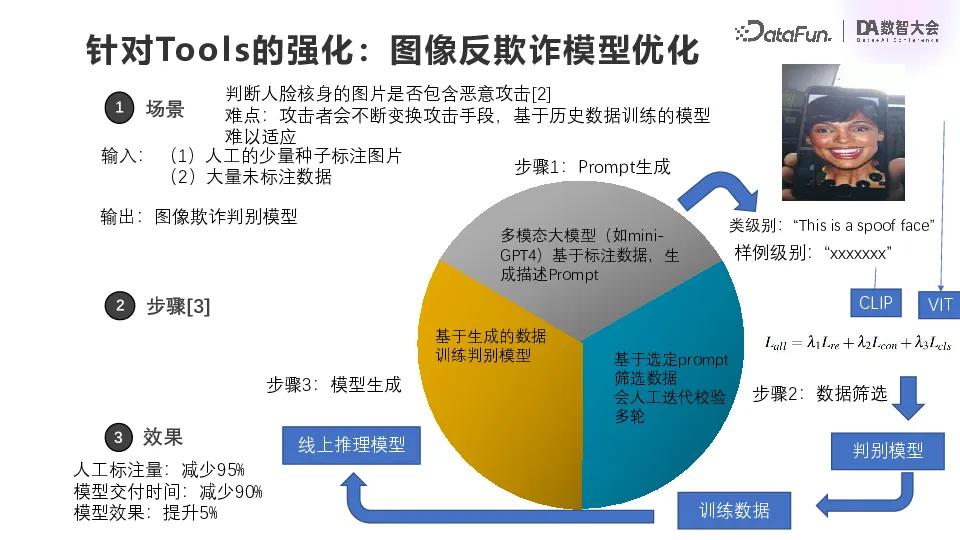
The second case is more typical, that is, image anti-fraud model optimization, aiming at the scene of KYC face body. Everyone has used face brushing, behind which is actually not a single model, but a combination of many models. It detects fraud, such as taking a screen or using a high-definition mask to pretend to be a particular person.
This looks like a simple image classification, and there are two problems with it. The first issue is domain adaptation. The user's face is sensitive data, we can not actually access the user's face data, only through the public data to train adaptation, such as the picture shown in the upper right corner of the above figure is a picture from the public data. However, the model trained with a large amount of public data may be far from the actual business scenario, such as lighting conditions, facial skin color, and may be far from the actual user. So generalization of the model can be a big problem
The second problem is that fraudsters are constantly changing their attack methods, so models must be agile and generalized. However, it is difficult to improve the performance of the model due to the lack of labeling personnel in the previous training process.
After having the large model, we manually annotated a small number of images and prompt words. For example, if the large model describes the face in the picture, the model will return that the face is in a phone and the phone is held by a human, which is very close to the understanding of the business person. Even if we use the public data for training, the multi-modal large model can extract the semantic features of the actual generalization through the alignment of the image mode and the text mode to ensure the generalization performance of the model in the real scene.
The specific implementation method is to extract the text features of the description generated by the large model through CLIP, and then use the vision Transformer to extract the features of the image itself, and then make special alignment. Here is the sum of the three cost functions. In the middle is the cost function of CLIP comparison learning, which is actually the comparison learning between text features and image features. The head and tail are the Loss functions of vision Transformer, one is Reconstruction Loss, the other is classification loss, and the three are weighted. When you look directly at the mask of attention, you will find that after such alignment, the corresponding mask of attention of the graph will focus on the understanding of the graph. Even if skin color changes or light conditions change, the model will still have some generalization ability.
After that is a discriminant model, which again takes the description of the mini GPT 4 as one of the inputs, so it is a bit slow, but it is sufficient, we use it to understand and label the training data, and then we can get a faster inference model online.
In addition to the excellent effect and generalization ability of this scheme, a more special point is that it is naturally connected with people's own thinking through the carrier of natural language. Even if our training data and the real scene seem far away, we can efficiently extract the truly generalized features, which greatly improves the delivery efficiency of the entire model [2][3].

In the original process, the business put forward a requirement, and to make an AI model, it required a lot of annotation work, and often our understanding of this field could not be injected into the data. But now, based on the big model, the features of the image are aligned with the language description, and then through the language vector, the business side's expectations can be aligned.
Here, the general knowledge carried by large models is utilized to generate training data; Also taking advantage of the command understanding capabilities of the large model, the domain expert directly injects his understanding of the case into the domain understanding by guiding the large model through natural language.
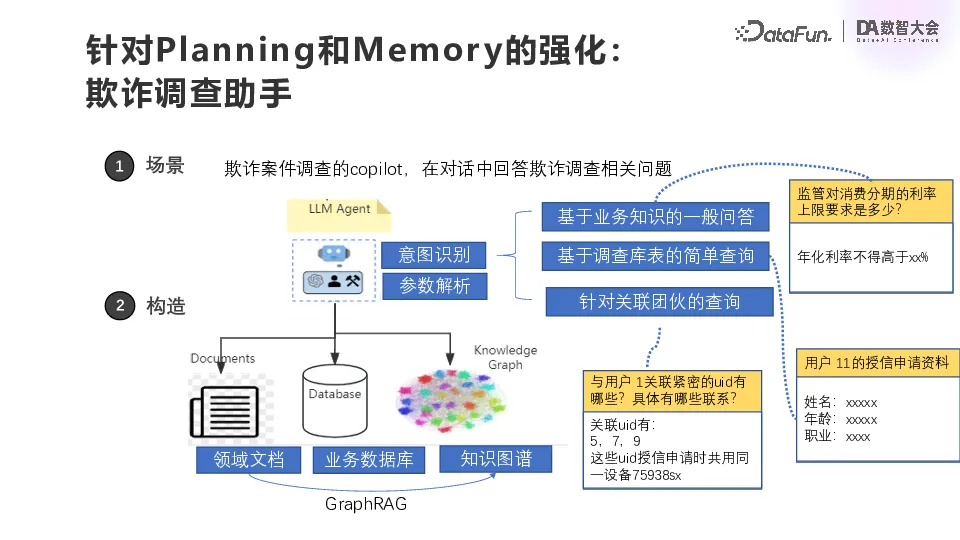
The second category is the strengthening of Planning and Memory, which is actually to reduce the burden and improve the efficiency of our business personnel. The first scenario is the anti-fraud investigation copilot, which addresses relevant issues through conversations with fraud investigators. Using GraphRAG technology, intention identification is carried out first, and the intentions here are basically fixed and enumerable. The first is a general question and answer based on business knowledge, the second is a simple query based on the survey database table, and the third is a query based on associated groups. After the intention identification is complete, the parameter is parsed according to the intention, and then the query is carried out.
Here the business knowledge is generally stored in the RAG vector library in the form of free documents, and the business library table is in the number of bins. At present, the company does not have a particularly complete data lineage, so a lot of data lineage information is actually placed in the domain documentation. So the first step might be to do a simple graph relationship extraction, usually with a preset prompt, such as some table information and association information, if available, to pull it out for a simple support.
This is the implementation of the Fraud Investigation Assistant scenario.
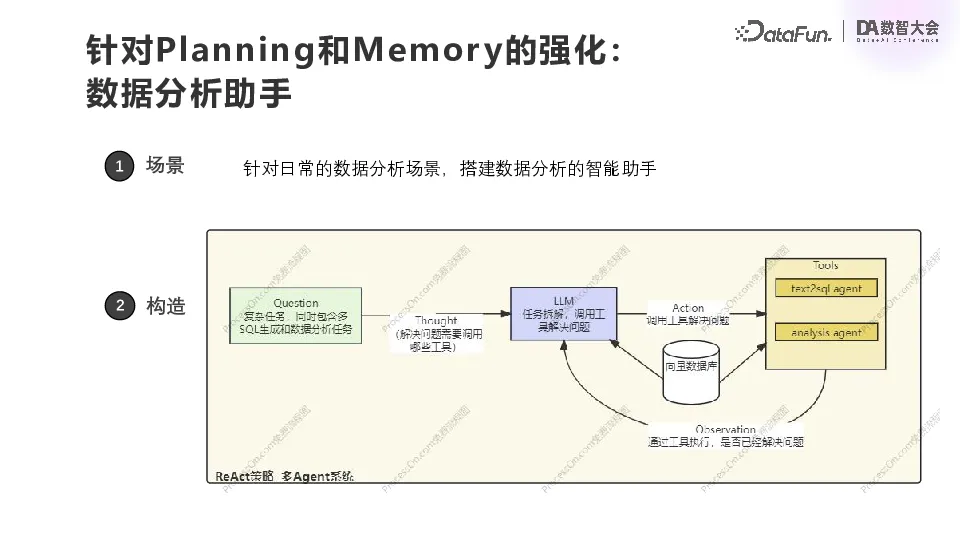
The second scenario is also a very general one, ChatBI, which is implemented based on Text2SQL. When there is a need for data analysis, you can ask directly. First of all, disassemble according to user questions and determine which tools need to be called. We currently have two tools, one is Text2SQL and the other is a simple visual analysis tool based on Pandas. Once the tool is selected, it relies on the tool to perform the corresponding action, calling the vector database to recall the document and some descriptive text pieces related to the domain. The result of each Agent's return determines whether the problem has been solved.
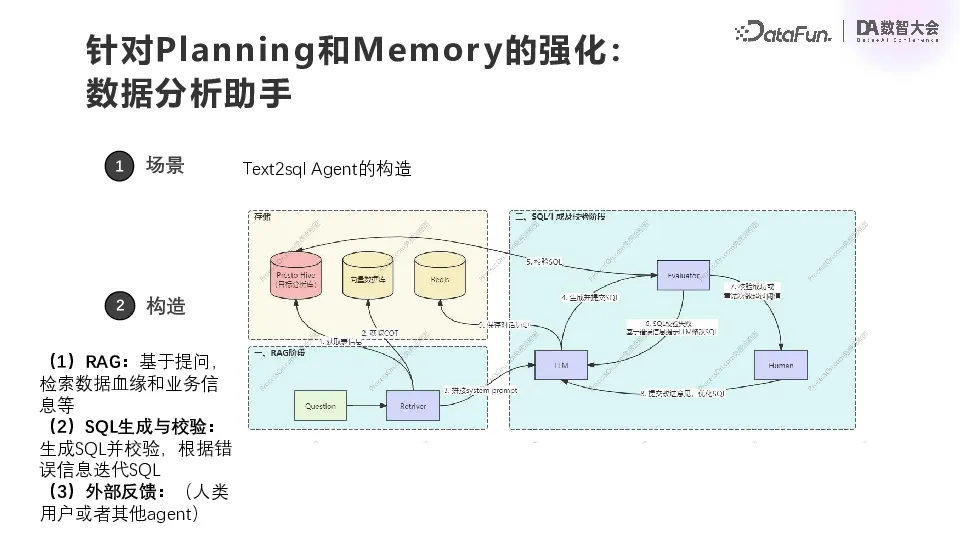
Inside this Text2SQL Agent, there will also be a small loop similar to the above. Our data analysis is based on Presto. Users will put their own documents into the vector database, and Redis will store the conversation history. First of all, based on the questions raised by the user, obtain the metadata information of the table and its own documents to obtain the corresponding text slice and some clues of the chain of thought, form a total prompt, input into the Agent of the large model, and then generate SQL, test SQL, execute SQL, modify SQL. Do this several times and then return the final result.
In the process of landing, we found a difficulty, the effect of this practice is OK for new SQL, but for some of the existing more complex SQL, we need to organize the documents well, and then do the corresponding recall, the Agent can have a better effect.
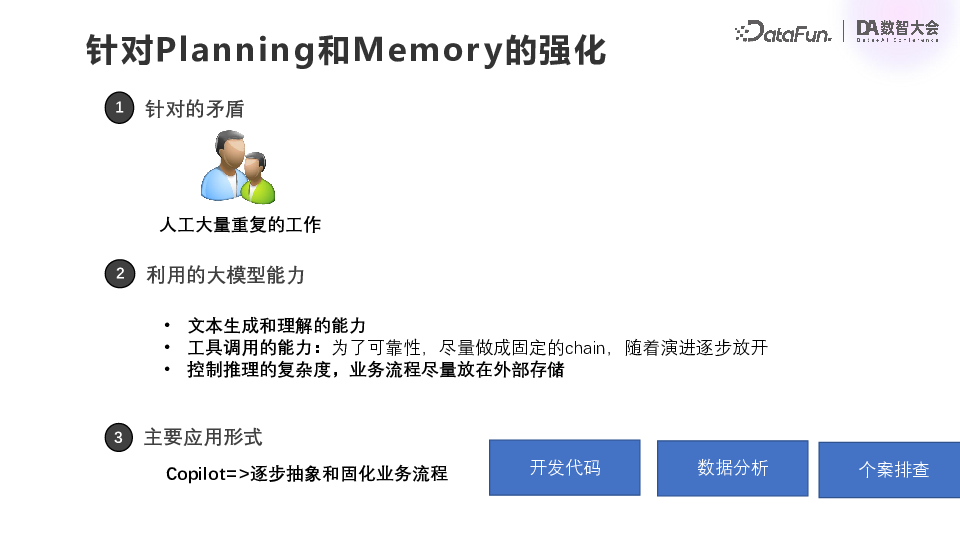
The Planning and Memory enhancement differs from the previous Tools enhancement in that it is not an optimization of a specific model, but rather a role, such as code development, data analysis, case review, or customer service. The enhancement of Planning and Memory is provided in the form of Copilot. First, an assistant is constructed, using the ability of text generation and understanding of the large model, the ability of tool call, and the existing documents to construct some structured knowledge as best as possible, so that the results of the large model are as close as possible to user expectations. This is done in the form of Copilot to assist the role with development, analysis, or research. Finally, a fixed process is abstracted based on these SQL or surveys.

Our agent landing steps can be summarized as:
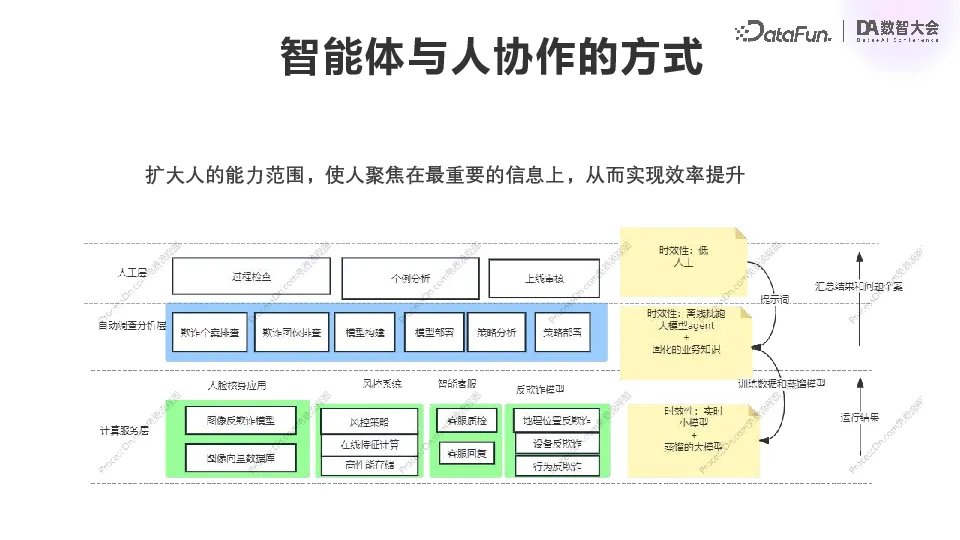
An important question in the process of landing is, what role should people play, and whether the agent system will completely replace the human? According to our experience and judgment on the future, big-model Agent can not completely replace people, but only expand the scope of people's ability. To a certain extent, big-model agent can replace tedious and repetitive work, and make people focus more on the core issues of business situation.
We have a core risk control and intelligence system, including various risk control, marketing, e-commerce and financial systems, which are fixed models and fixed business logic. In the middle are fraud investigation, model construction, strategy analysis and other businesses corresponding to each department. We expect to solidify the standardized parts of these work by gradually introducing agents, and finally realize them by agents. People can gather around the whole business as a whole, as well as some important individual cases.
After discovering some new phenomena in the business, business personnel will try to summarize them into prompt words, and then guide the Agent in the middle to mine data, generate data, and do some corresponding analysis and summary. This analysis generates new training data and distills more efficient models, which are then deployed to our online real-time system. In the process, real-time statistics and monitoring of the operation results will be carried out, and then the results and some abnormal cases will be summarized to the manual layer. This is the structure of the agent system that we want to achieve.
That's all for this time. Thank you.
[1] Lilian Weng (2023, June 23), LLM Powered Autonomous Agents at https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/.
[2]Zhang Y, Yin Z F, Li Y, et al. Celeba-spoof: Large-scale face anti-spoofing dataset with rich annotations[C]//Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XII 16. Springer International Publishing, 2020: 70-85.
[3]Fang, H., Liu, A., Jiang, N., Lu, Q., Zhao, G., & Wan, J. (2024, April). VL-FAS: Domain Generalization via Vision-Language Model For Face Anti-Spoofing. In ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 4770-4774). IEEE.

2025-02-17

2025-02-14

2025-02-13
13004184443
Room 607, 6th Floor, Building 9, Hongjing Xinhuiyuan, Qingpu District, Shanghai
gcfai@dongfangyuzhe.com


WeChat official account
friend link



13004184443
立即获取方案或咨询
top