Home > Information > News
#News ·2025-01-03
This article is reprinted with the authorization of AIGC Studio public account, please contact the source for reprinting.
Today, we introduce UniReal, a unified image production and editing method proposed by the University of Hong Kong and Adobe, which unifies a variety of image tasks into a paradigm of video generation, and learns real dynamics and changes in large-scale video, achieving the best level in command editing, image customization, image combination and other tasks.

 picture
picture
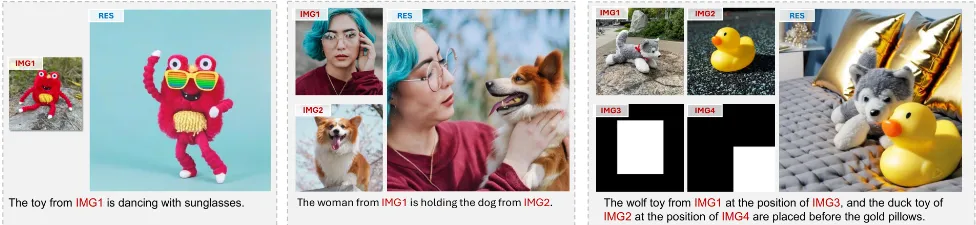
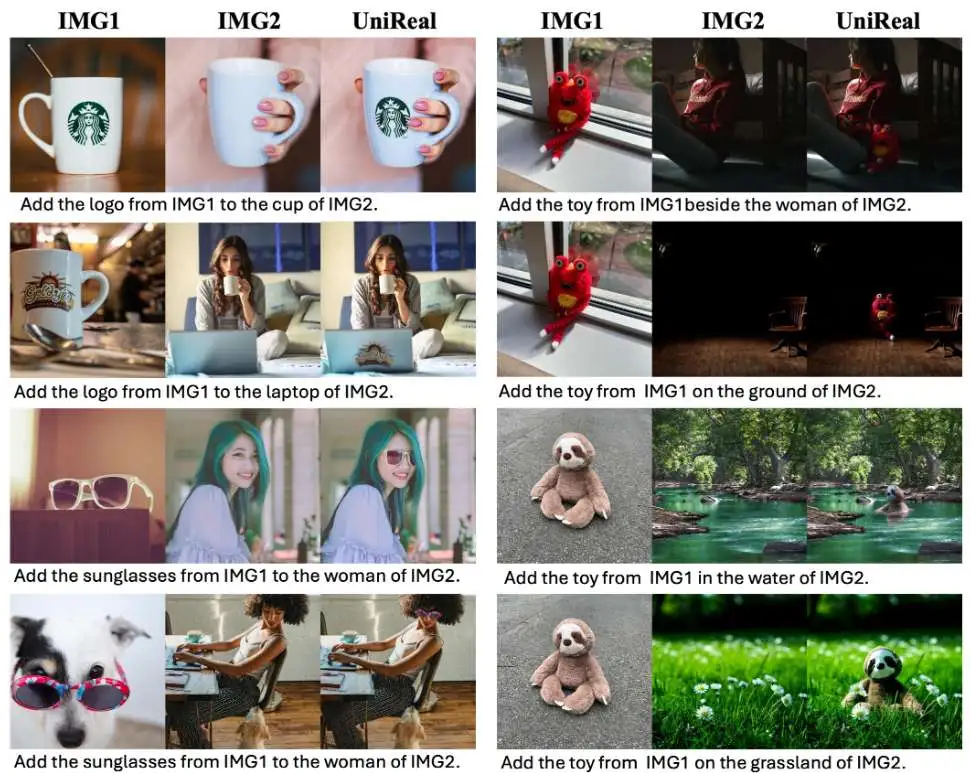
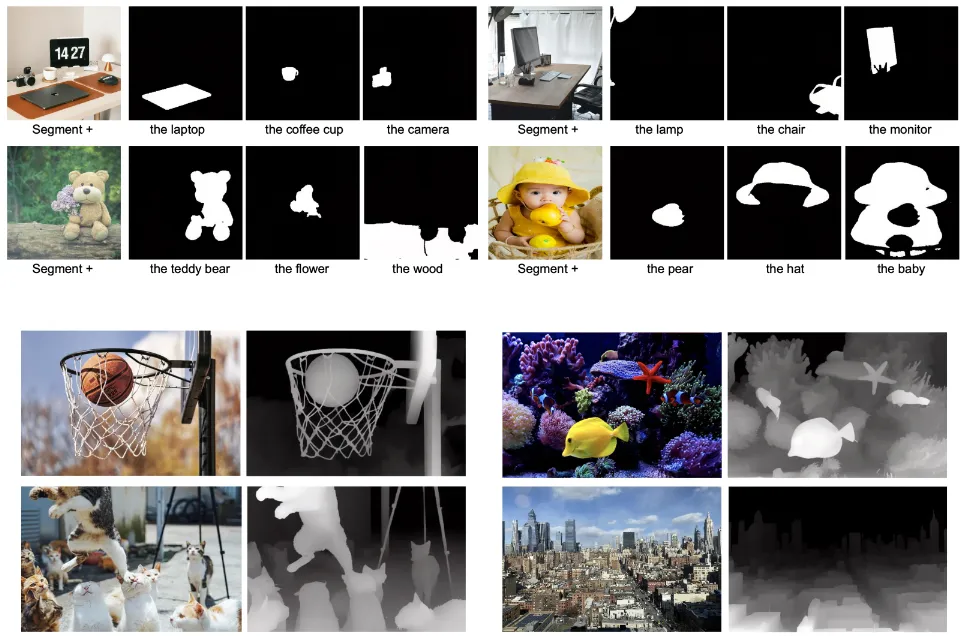
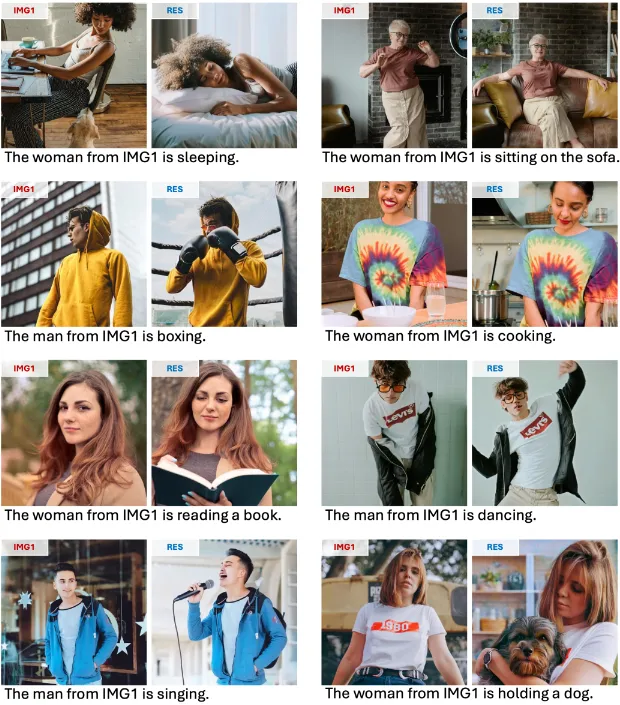
Above is a demonstration of UniReal's versatility. As a universal framework, UniReal supports a wide range of image generation and editing tasks within a single model, ADAPTS to different input and output configurations and produces highly realistic results, which can effectively handle challenging scenes such as shadows, reflections, lighting effects, object pose changes, and more.
The paper proposes a unified framework, UniReal, designed to solve various image generation and editing tasks. Existing solutions often vary from task to task, but the basic principle is the same: maintain consistency between inputs and outputs while capturing visual variations. Inspired by recent video generation models that effectively balance consistency and variation between frames, we propose a unified approach that treats image-level tasks as discontinuous video generation. Specifically, different numbers of input and output images are treated as frames, enabling seamless support for image generation, editing, customization, compositing and other tasks. Although designed for image-level tasks, it leverages video as a scalable source of general supervision. UniReal learns world dynamics from large-scale video, demonstrating advanced capabilities for dealing with shadows, reflections, postural changes, and object interactions, while also demonstrating emerging capabilities for new applications.
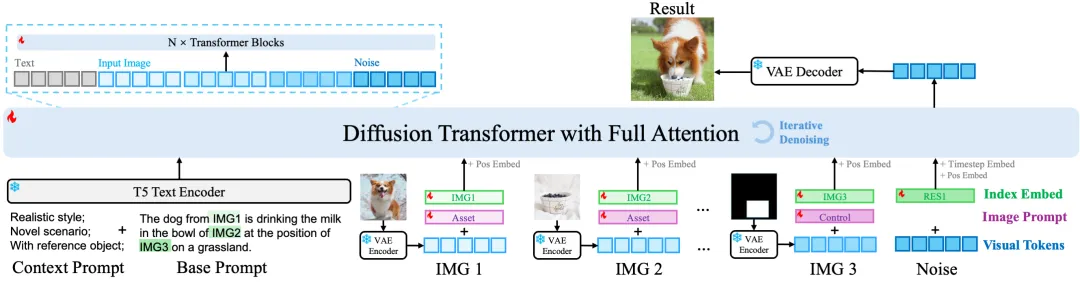 UniReal sets the task of image generation and editing to discontinuous frame generation. First, the input image is encoded into the potential space by the VAE encoder. Then, the image potential and noise potential are patched into visual markers. Index embeddings and image hints (assets/canvas/controls) are then added to the visual markup. Meanwhile, contextual and basic prompts are handled by the T5 encoder. Concatenate all potential patches and text embeddings into a long 1D tensor and send them to the converter. Finally, the denoising result is decoded to obtain the desired output image.
UniReal sets the task of image generation and editing to discontinuous frame generation. First, the input image is encoded into the potential space by the VAE encoder. Then, the image potential and noise potential are patched into visual markers. Index embeddings and image hints (assets/canvas/controls) are then added to the visual markup. Meanwhile, contextual and basic prompts are handled by the T5 encoder. Concatenate all potential patches and text embeddings into a long 1D tensor and send them to the converter. Finally, the denoising result is decoded to obtain the desired output image.






2025-02-17

2025-02-14

2025-02-13
13004184443
Room 607, 6th Floor, Building 9, Hongjing Xinhuiyuan, Qingpu District, Shanghai
gcfai@dongfangyuzhe.com


WeChat official account
friend link



13004184443
立即获取方案或咨询
top