Home > Information > News
#News ·2025-01-09
This article is reproduced by the authorization of the 3D Vision Heart public number, please contact the source.
Monocular Depth Estimation (MDE) has received a lot of attention due to its simplicity, low cost, and ease of deployment. Unlike traditional depth sensing technologies such as LiDAR or stereovision, MDE requires only one RGB image as input, making it highly attractive in multiple applications such as autonomous driving, virtual reality, and image synthesis. However, this also presents a significant challenge: how to achieve superior generalization ability in a wide range of application scenarios to effectively deal with the diversity and complexity of scene layout, depth distribution, lighting conditions, and other factors. This task is not easy, because different scenarios and conditions often bring about very large changes.
In recent years, zero-shot monocular depth estimation has been developed into two main methods: data-based method and model-based method. Data-based method: Relying on a large number of image-depth pairs, the mapping between image and depth is obtained by training. However, this process is very time consuming and requires huge computing resources. In contrast, model-based approaches show more efficient performance by utilizing pre-trained backbone networks, especially in the context of Stable Diffusion models. For example, Marigold has achieved impressive results in generalization and detail retention by refactoring depth estimates into a diffusion denoising process. However, the iterative denoising process results in a lower inference speed.
Despite significant advances in the application of diffusion models to monocular depth estimation, few studies have delved into how to most effectively adapt generated features to discriminative tasks. Therefore, this paper focuses on the feature representation in the diffusion model, especially on how to optimize the feature representation capability of the denoising network. Typically, the diffusion model consists of an image-to-latent space codec and a denoising network. The former compresses the image into the potential space and reconstructs it, while the latter is responsible for sensing and reasoning about the scene. Through experiments, it is found that the main bottleneck lies in the feature representation capability of the denoising network. In fact, the reconstruction task used to pre-train the denoising network causes the model to focus too much on texture details, resulting in unreal textures in the depth prediction. Therefore, how to enhance the feature representation capability of de-noising networks and reduce the dependence on irrelevant details is a key problem in applying diffusion models to depth estimation tasks.
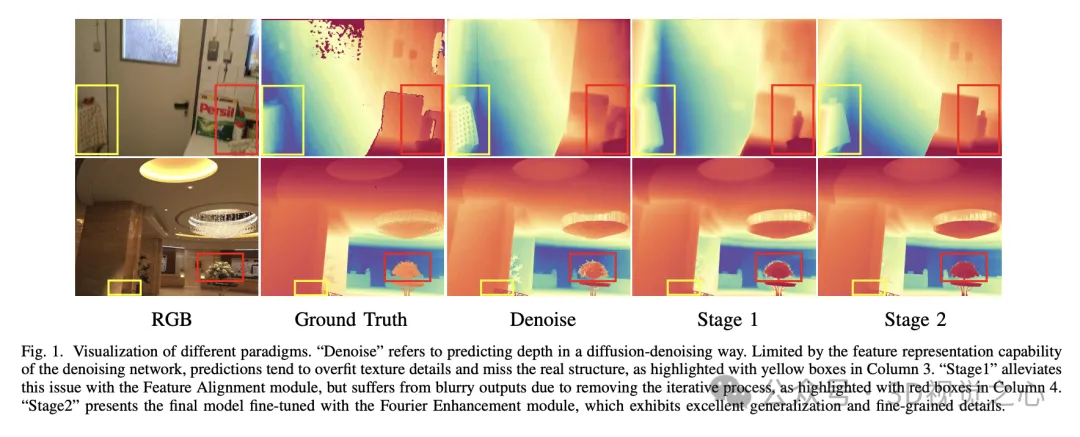
DepthMaster [1] is a customized single-step diffusion model designed to improve the generalization and detail retention capabilities of depth estimation models.
With these optimizations, our method outperforms other diffusion-based depth estimation methods on multiple datasets, achieving the latest performance.
Major contributions:
Projects link: https://indu1ge.github.io/DepthMaster_page/
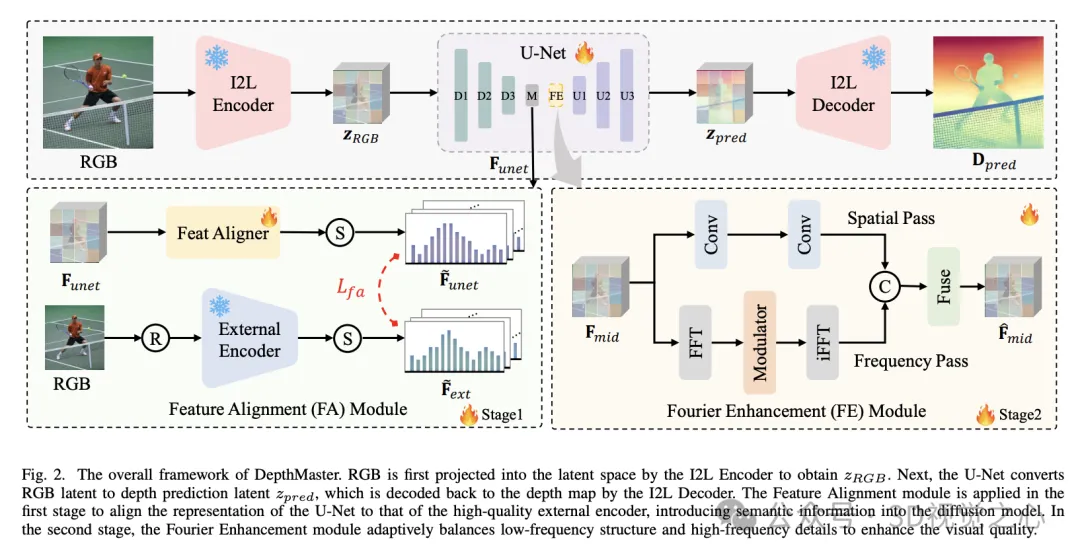

The stable diffusion v2 consists of two main components: the I2L encoder-decoder and the de-noising U-Net. The I2L encoder-decoder is responsible for feature compression and is designed to reduce inference time and training costs. Trained by image reconstruction, it mainly captures low-level features. In contrast, U-Net is responsible for recovering images from noisy images, so that it has scene perception and reasoning capabilities. However, because U-Net is trained through reconstruction tasks, it tends to overemphasize detailed textures, which leads to pseudo-texture problems in depth prediction (as shown in Figure 1). Therefore, we introduce semantic regularization to enhance U-Net's scene representation capability and prevent overfitting of low-level color information.

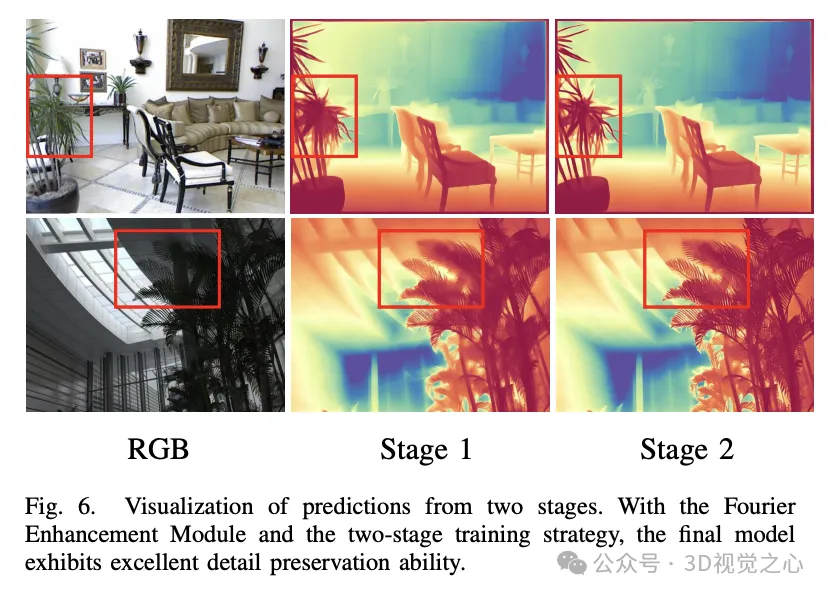
The one-step paradigm effectively speeds up the inference process by avoiding multi-step iterative processes and multi-run integrations. However, the fine-grained features of the output of diffusion models usually come from the iterative refinement process. As a result, the one-step model has fuzzy predictions when processed (as shown in Figure 1). To alleviate this problem, we propose a Fourier enhancement module that operates in the frequency domain to enhance high frequency detail to effectively simulate learning in a multi-step denoising process.


Since the depth reconstruction accuracy of the I2L encoder-decoder is already high enough, we will focus on fine-tuning U-Net. Experiments show that the supervision of latent space helps the model to better capture the global scene structure, while the supervision at the pixel level helps to capture fine-grained details, but also introduces the distortion of the global structure. Based on these observations, we propose a two-stage training strategy.
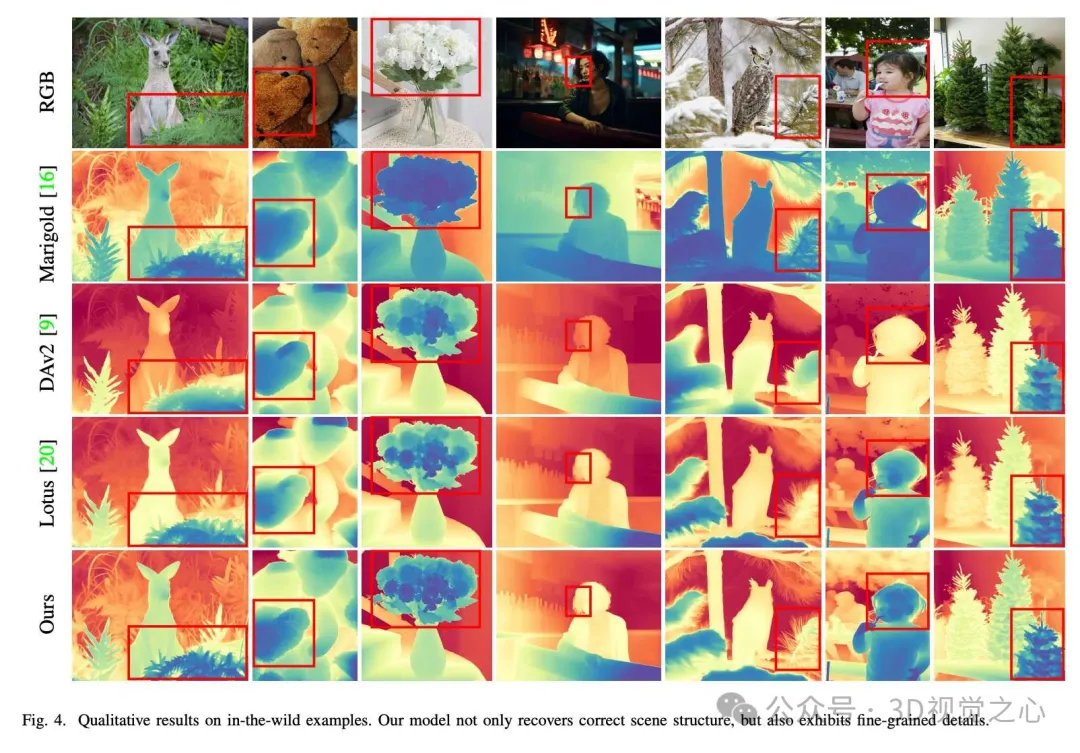

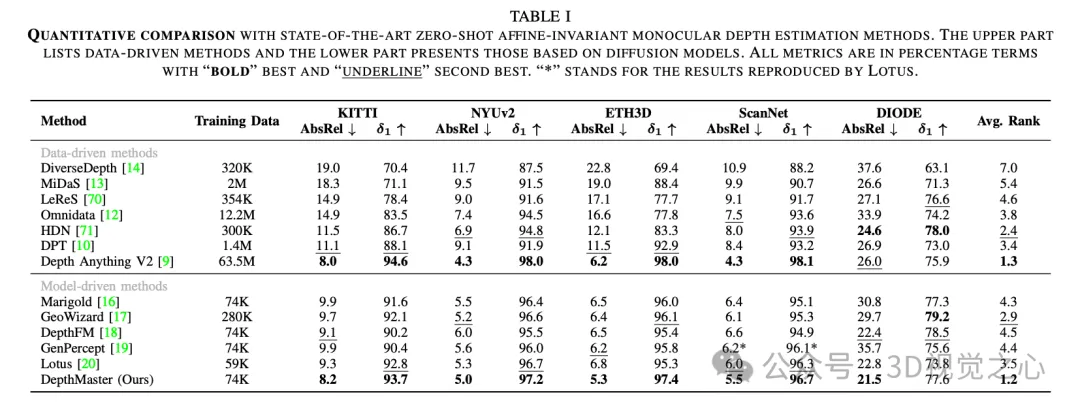
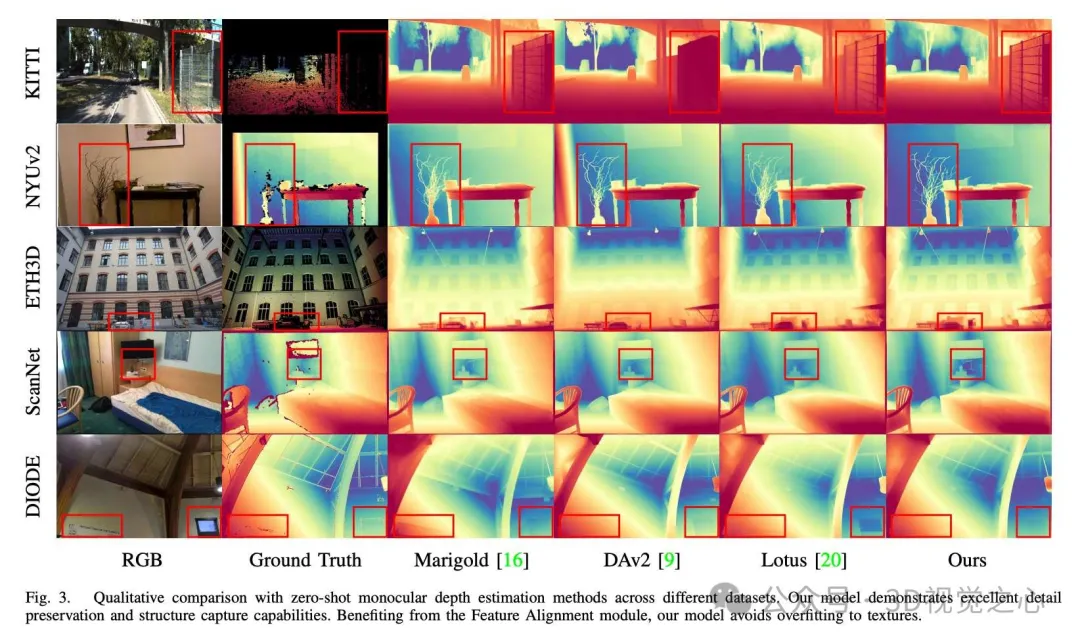


DepthMaster is used to customize the diffusion model to fit the depth estimation task. By introducing the feature alignment module, the overfitting problem of texture details is effectively alleviated. In addition, the ability to retain fine-grained details is significantly enhanced by the Fourier enhancement module operating in the frequency domain. Thanks to these careful designs, DepthMaster has achieved significant improvements in zero-sample performance and inference efficiency. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach, which is up to date in terms of generalization power and detail retention, outperforming other diffusion model-based approaches, and performing well on a variety of datasets.

2025-02-17

2025-02-14

2025-02-13
13004184443
Room 607, 6th Floor, Building 9, Hongjing Xinhuiyuan, Qingpu District, Shanghai
gcfai@dongfangyuzhe.com


WeChat official account
friend link



13004184443
立即获取方案或咨询
top