Home > Information > News
#News ·2025-01-08
The current 3D models generated by AI already have a fairly high quality.
But these generated results are usually just some representation of a single object (such as an implicit neural field, Gaussian mixture, or grid), and do not contain structural information.
For professional applications and creative workflows, in addition to high-quality shapes and textures, there is a need for "parts-level 3D models" that can be operated independently.
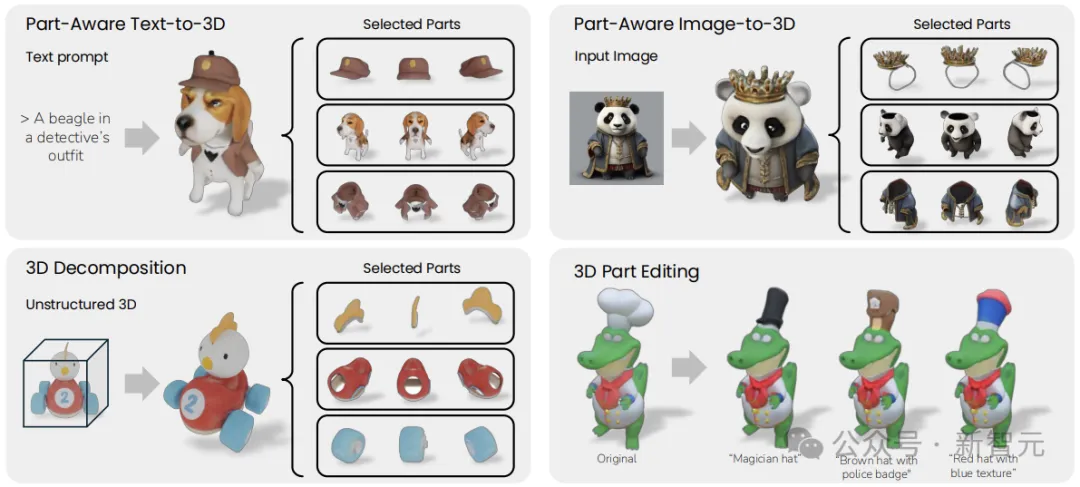
As in the examples above, a 3D model should consist of multiple meaningful parts that can be separated, combined, and edited.
The effect shown above is PartGen, a new multi-view diffusion model developed by researchers at Meta and the University of Oxford.
Address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.18608
Project address: https://silent-chen.github.io/PartGen
PartGen can use text, images, or unstructured 3D objects as input to generate 3D models that are "substructurally separable" as described above.
Similar to some of the SOTA generation workflows, PartGen uses a two-stage approach to remove ambiguity around parts segmentation and reconstruction:
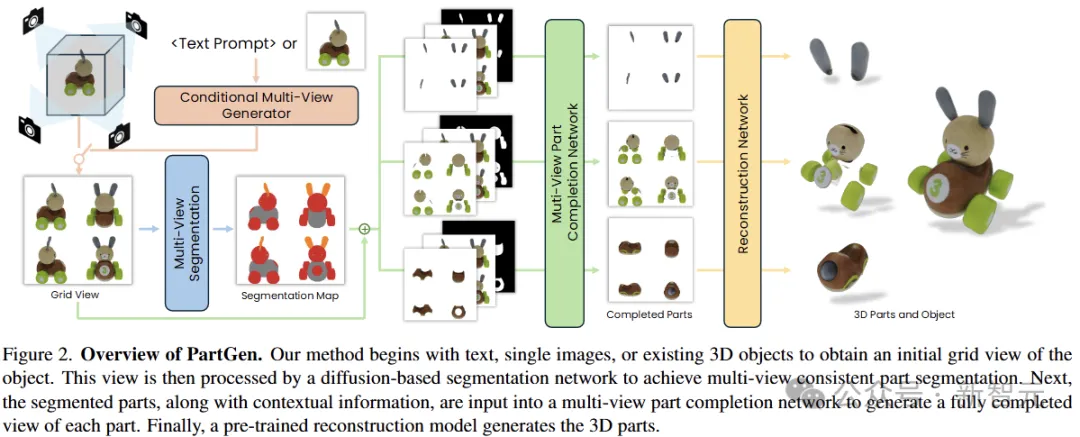
First, the multi-view generator generates multiple views of the 3D object according to the given conditions, and extracts a set of reasonable and consistent view partial segmentation by the first multi-view diffusion model, dividing the object into multiple parts.
A second multi-view diffusion model then separates each part, fills in the occlusion and feeds into the 3D reconstruction network, 3D reconstruction of these complementary complete views.
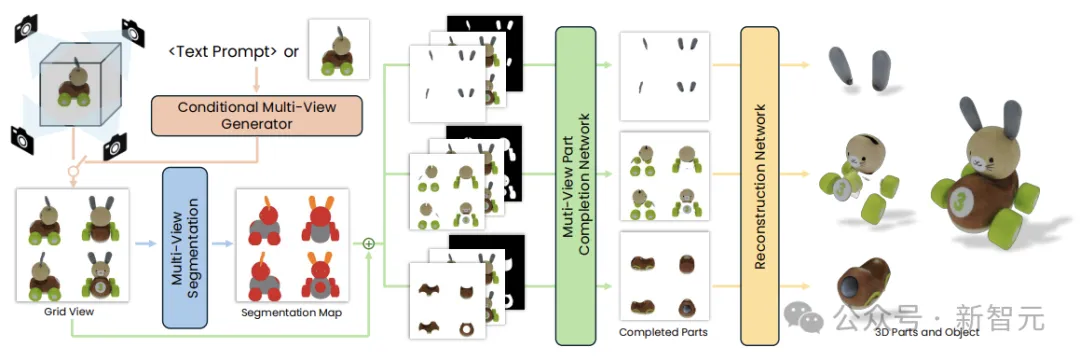
PartGen considers the context of the entire object during the build process to ensure that the parts are tightly integrated. This generative completion model can make up for the information lost due to occlusion and restore the completely invisible part.
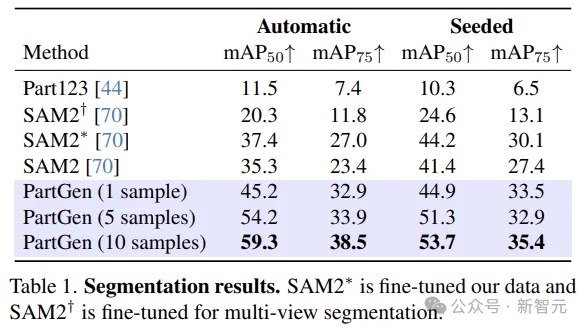
The authors evaluated PartGen on synthetic as well as real 3D assets, as shown in the figure, and its performance significantly outperforms previous similar methods.
The authors also deployed PartGen to real downstream applications, such as 3D part editing, to prove the strength of the model.
Parts are important because they can support reuse, editing, or animation.
Human artists naturally think in this light when making 3D models.
For example, a model of a person can be broken down into clothes and accessories, as well as various anatomical features (hair, eyes, teeth, limbs, etc.).
The information and function carried by the part is also important, for example, different parts may have different animations or different materials.
Parts can also be individually replaced, deleted or edited. In video games, for example, characters change weapons or clothes.
In addition, because of their semantic meaning, parts are also important for 3D understanding and applications such as robotics, embodied artificial intelligence, and spatial intelligence.
PartGen upgraded the existing 3D generation method from unstructured to a component assembly approach, solving two key problems:
1) How to automatically split 3D objects into multiple parts;
2) How to extract high-quality, complete 3D parts, even when the appearance is partially obscured, or not visible at all.
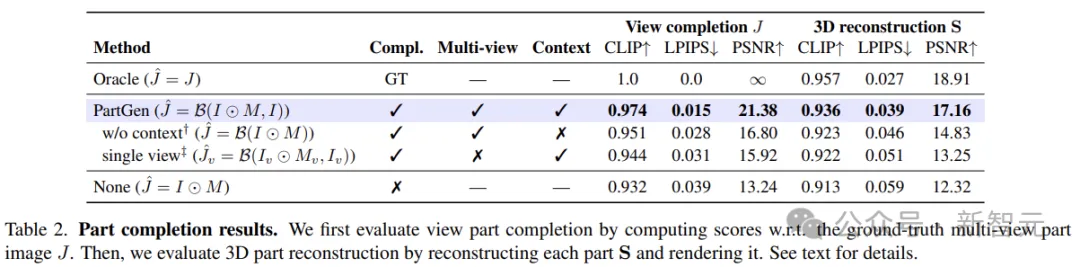
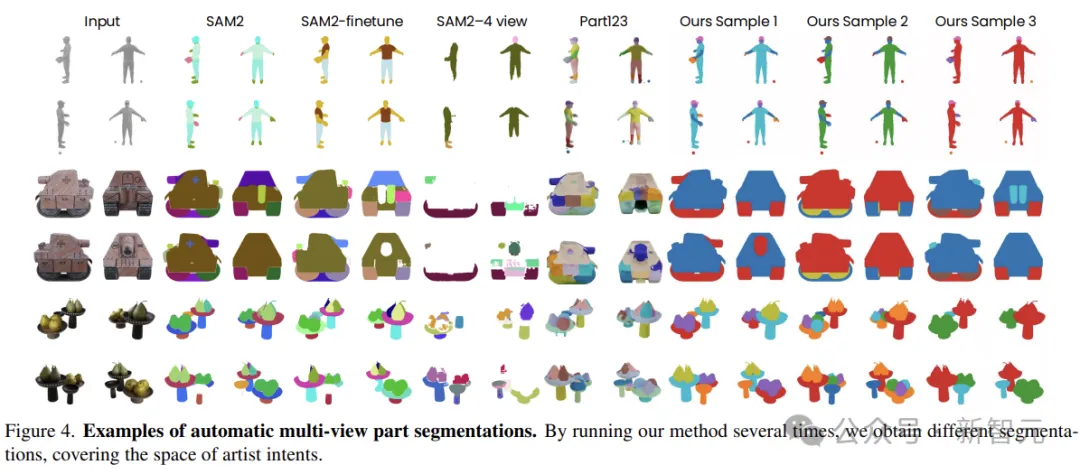
There is no "gold standard" for 3D object segmentation. Therefore, segmentation methods should model the distribution of reasonable partial segmentation rather than individual segmentation.
This task can be learned using probabilistic diffusion models to effectively capture and model this ambiguity.
As the first stage of the generation process, the researchers translate the part segmentation into a stochastic multi-view-consistent colouring problem using a fine-tuned multi-view image generator, Generate color-coded segmentation plots in multiple views of 3D objects.
The authors do not assume any deterministic parts taxonomy - the segmentation model learns from the vast amount of data created by the artist how to decompose an object into multiple parts.
Considering the majority of the graph images as input, the task of the model is to predict the mask of multiple parts. Given a map, the split map is rendered as a multi-view RGB image, and then the pre-trained model is fine-tuned.
The authors use VAE to encode multi-view images into the potential space and stack them with the noise potential space as input to the diffusion network.
This method has two advantages: first, it uses a pre-trained image generator to ensure that the view is inherently consistent; Second, the generation method allows for simply resampling from the model to make multiple reasonable partitions.
For the second problem, rebuilding the split part in 3D, the common approach is to mask the part in the existing object view and then restore it using the 3D reconstruction network.
However, when the part is heavily obscured, this task is equivalent to non-modal reconstruction, which is highly fuzzy and not well addressed by deterministic reconstruction networks.
This article suggests fine-tuning another multi-view generator to complete a partial view, taking into account the context of the entire object.
Similar to the previous stage, the researchers applied the pre-trained VAE to the mask and context images respectively, producing 2 × 8 channels, and stacked them with the 8D noise images and uncoded partial masks to obtain 25 channel inputs for the diffusion model.
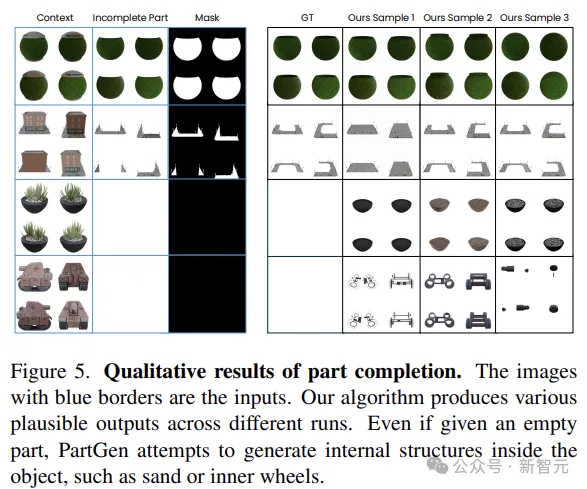
In this way, parts can be reliably reconstructed even if they are only partially visible or even invisible in the original input view. In addition, the generated parts can fit together nicely to form a coherent 3D object.
The final step is to reconstruct the parts in 3D. Because the parts view is already complete and consistent, the predictions can simply be generated using the reconstruction network, and no special fine-tuning is required for the model at this stage.
To train the model, the researchers built the dataset from a collection of assets generated by 140k 3D artists (licensed from commercial sources for AI training). The sample object in the dataset is shown in Figure 3.
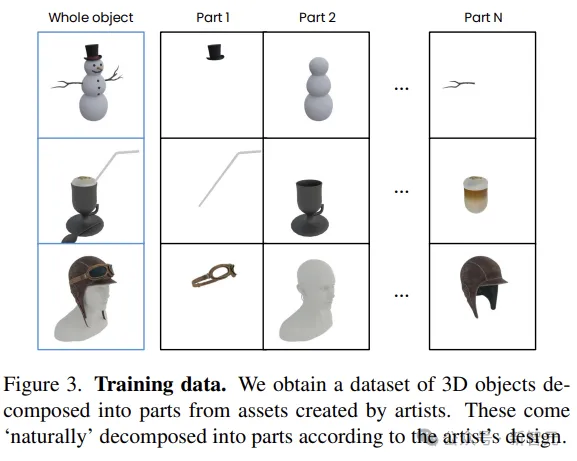
For the three models involved in fine tuning in the method, the data preprocessing method of each model is different.
In order to train the multi-view generator model, the target multi-view image (consisting of 4 views) must first be rendered to the complete object.
The authors colored four views from orthogonal azimuths and 20-degree elevation angles and arranged them in a 2 × 2 grid.
Under text conditions, the training data consists of multi-view image pairs and their text titles, 10k of the highest quality assets are selected, and their text titles are generated using a CAP3D-like workflow.
In the image condition, using all 140k model data, set the random sample to appear as a single render.
In order to train the part segmentation and completion network, it is also necessary to render multi-view part images and their depth maps.
Because different creators have different ideas about partial decomposition, authors filter out overly granular parts of the dataset that may lack semantics (first eliminating parts that occupy less than 5% of the object's volume, then removing assets that have more than 10 parts or are made up of a single whole).
The final dataset contains 45k objects (210k parts).
The following figure shows several examples of applications: parts-aware text to 3D generation, parts-aware image to 3D generation, and real-world 3D object decomposition.
As shown in the figure, PartGen can efficiently generate 3D objects with different parts, even in cases of heavy overlap, such as gummy bears.
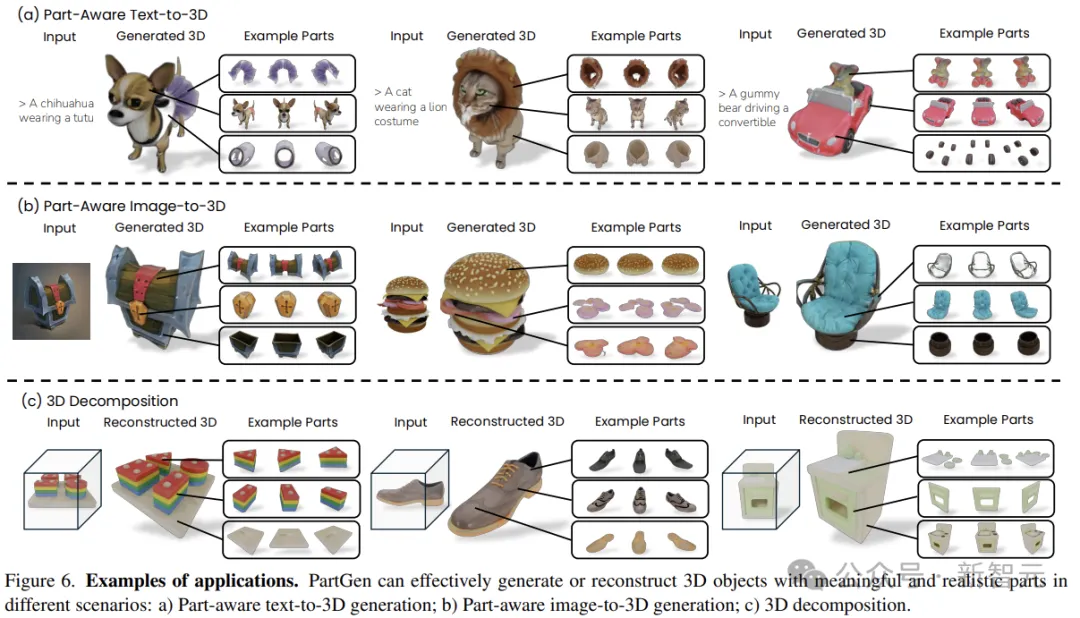
Given a 3D object from GSO (Google Scanned Objects) and rendered different views to obtain an image grid, the last line of Figure 6 shows that PartGen can efficiently decompose real-world 3D objects.
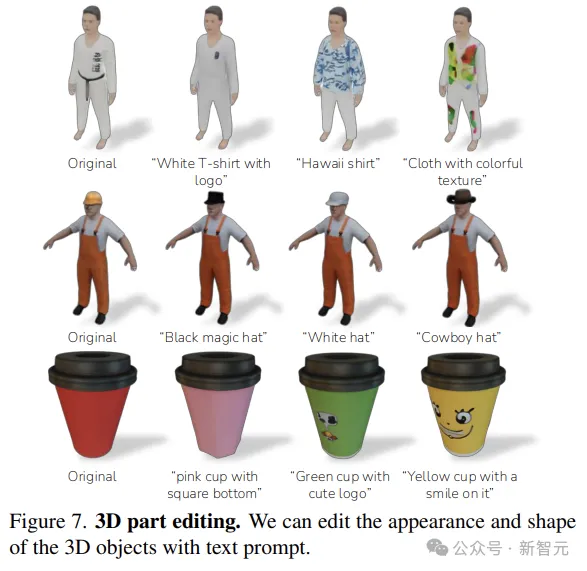
When 3D objects are decomposed, they can be further modified with text input. As shown in Figure 7, PartGen can effectively edit the shape and texture of a part based on text prompts.

2025-02-17

2025-02-14

2025-02-13
13004184443
Room 607, 6th Floor, Building 9, Hongjing Xinhuiyuan, Qingpu District, Shanghai
gcfai@dongfangyuzhe.com


WeChat official account
friend link



13004184443
立即获取方案或咨询
top