Home > Information > News
#News ·2025-01-06
Radio Map (RM) is a very promising technology to obtain path loss through location information, which is important for reducing the communication cost of path loss estimation in 6G network applications.
Previous approaches to RM construction either required a lot of computational resources or relied on expensive sample-based path loss measurement methods.
Although Neural Network (NN) -based methods can efficiently construct RM without sampling, their performance is still not optimal, mainly due to the deviation between the generation characteristics of the RM construction problem and the discriminant modeling adopted by existing neural network-based methods.
In order to improve the performance of RM construction, researchers from Xidian University, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and University of Waterloo for the first time conducted a comprehensive theoretical analysis of the reasons why RM construction is a generative problem from two perspectives of "data characteristics" and "neural network training methods". A new method based on de-noising diffusion model (RadioDiff) is proposed to model the non-sampling RM construction problem as a conditional generation problem in order to achieve high-quality RM construction.

The thesis links: https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.08593
Code repository: https://github.com/UNIC-Lab/RadioDiff
In addition, in order to enhance the ability of the diffusion model to extract features from the dynamic environment, attention U-Net with adaptive fast Fourier transform module is used as the backbone network, which significantly improves the ability of extracting features from the dynamic environment. At the same time, the decoupling diffusion model is used to further improve the performance of RM construction.
In summary, the contribution of this paper is as follows:
Diffusion model
The diffusion model is a generative model based on Markov chains that recovers data by learning a de-noising process step by step.
How the diffusion model works: The core idea of the diffusion model is to gradually "diffuse" the raw data into noise through a series of steps, and then through the reverse process - that is, gradually remove the noise from the data with the noise added to it to generate the raw data. This process can be divided into two main stages.
Forward diffusion process: The raw data goes through a Markov chain of multiple time steps, and at each time step, Gaussian noise is added to the data according to a certain probability distribution. After T steps, the raw data is completely converted to random noise.
Reverse denoising process: When generating data, the diffusion model first creates an unstructured vector of noise from a prior distribution and then removes these noises in reverse chronological order through a trained neural network.
Forward diffusion process of RM
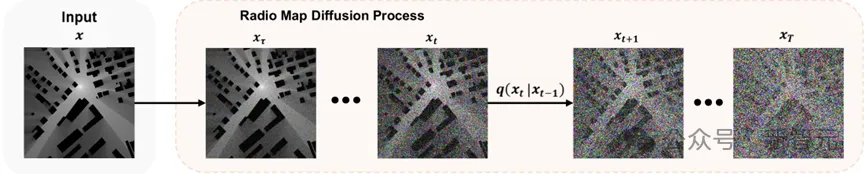
From the perspective of data features and training methods, and from the perspective of statistical learning and training methods, the construction of RM is a condition generation problem.
System architecture
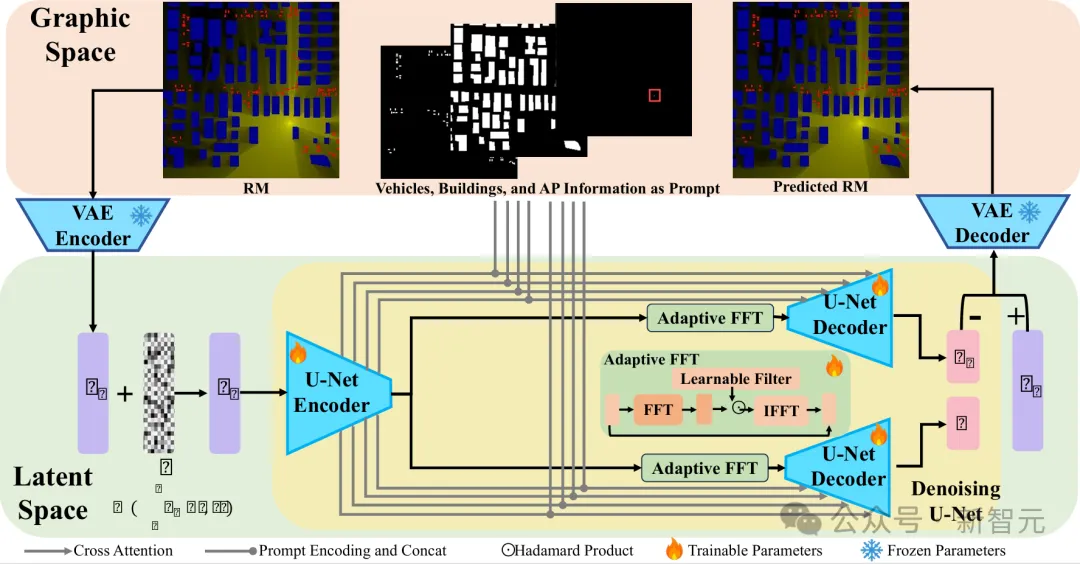
In the Radiodiff framework, VAE is used to encode RM as a potential vector, thereby reducing the dimension of the input/output space of the denoising diffusion model.
The framework uses a U-Net architecture consisting of encoders and decoders to facilitate the denoising process. The prompt is represented as a grayscale map with three channels, each describing the characteristics of the building, vehicle, and AP. After encoding the prompts, they are connected to the U-Net network, enabling the model to generate RM under ambient conditions.
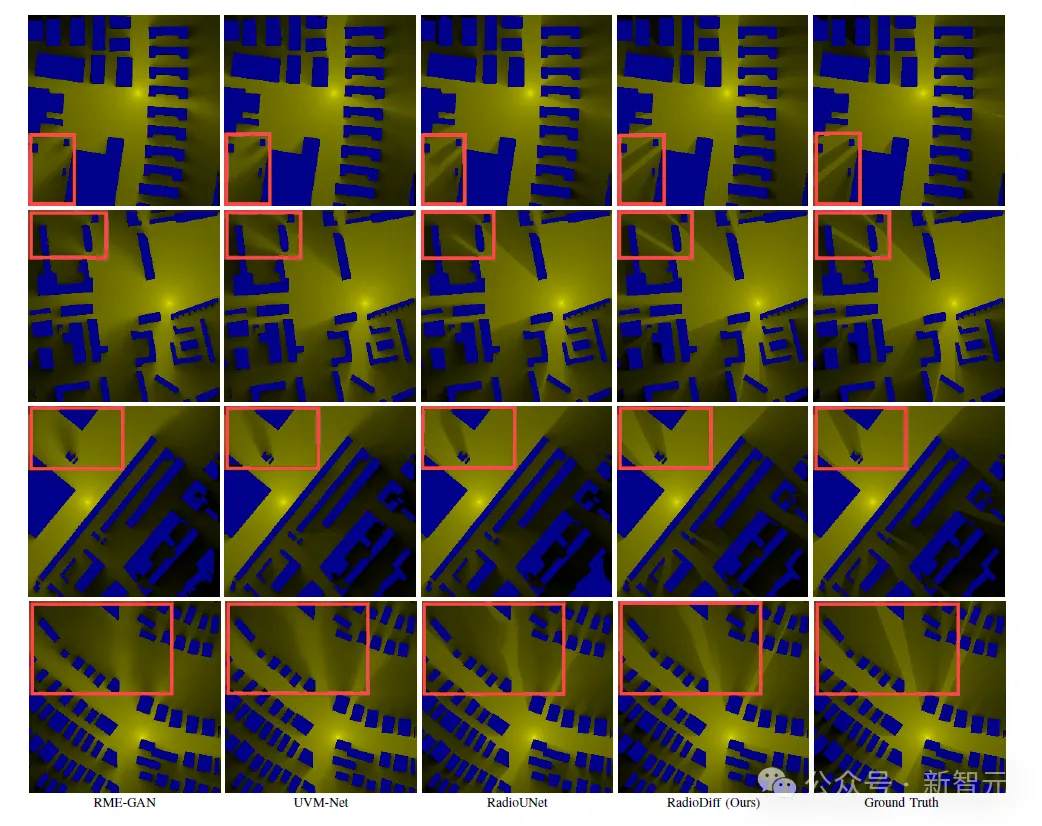
Effect comparison
In order to evaluate the proposed RadioDiff model, it is compared with other methods. To ensure a comprehensive comparison of the experiments, CNN-based, GAN-based, and MAMBA-based methods were compared, respectively, which represent the main architectures currently used in deep learning-based RM reconstruction tasks.
For the detailed parameter Settings of the comparison model, the training and test data will be consistent with RadioDiff. The following method is used for comparison, where SRM is static RM and DRM is dynamic RM.
Comparison of SRMS constructed by different methods
MSE: mean square error, calculated by averaging the squared variance between the pixel intensity of the original image and the final image. NMSE (Normalized MSAE), RMSE (square root of MSE). In addition, this paper introduces structural similarity index (SSIM) and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) as additional measures. The SSIM evaluates the preservation of structural information to emphasize the accuracy of the reconstruction of structural details, while the PSNR measures the signal-to-noise ratio to assess the fidelity of the RM construction, especially in the reconstruction of edge signals.
Quantitative comparison
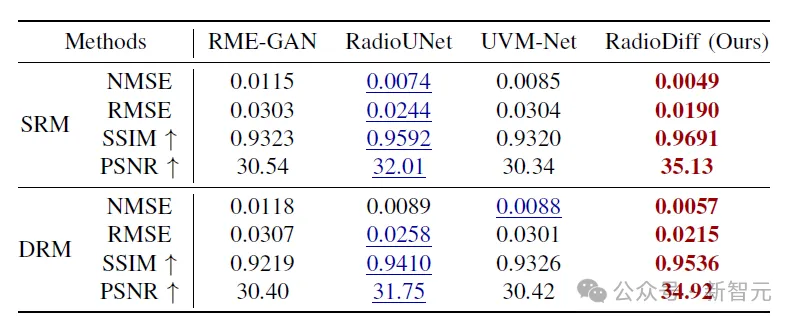
Comparison of SRM: The first part of the table and the figure provide quantitative comparison of the RadioMapSeer-Test dataset for SRM scenarios. This model is superior to other methods in error indicators (i.e., NMSE and RMSE) and structure indicators (i.e., SSIM and PSNR), indicating that our prediction and generated RM are more accurate. RadioDiff performs well on PSNR metrics, showing that it generates RM with clearer and sharper structural edges than other methods.
Comparison of DRM constructed by different methods
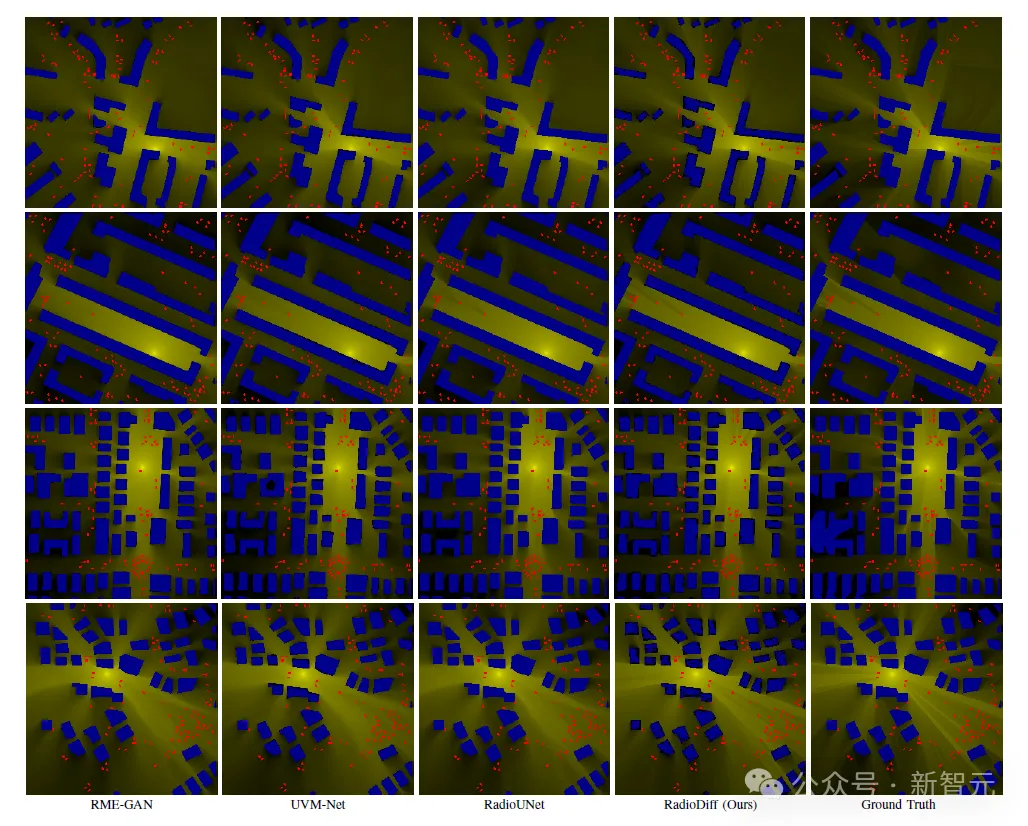
Comparison of DRM: As shown in the figure, the quantitative comparison of RadioMapSeer test data set in DRM scenario is given. In DRM scenarios, the model must take into account other dynamic environmental factors. Despite the general decline in performance, the table shows that RadioDiff consistently delivers the best results across all metrics.
RadioDiff models show greater sensitivity to dynamic environmental factors such as vehicles, while RME-GAN, RadioUNet, and UVM-Net models struggle to cope with these factors, often resulting in significant blurring and distortion.
Study on AFT ablation
To further improve the model's performance, the researchers added AFT to the model
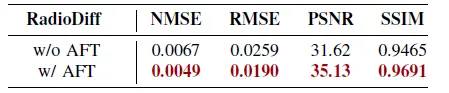
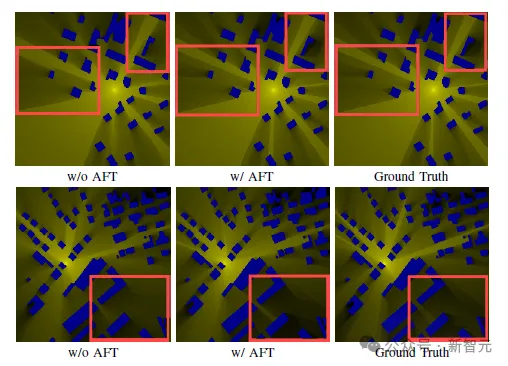
The qualitative results show that the addition of AFT further improves the sensitivity of the model to edge signals, making RM images have more accurate edges, and more robust results can be obtained when multiple signals overlap.

2025-02-17

2025-02-14

2025-02-13
13004184443
Room 607, 6th Floor, Building 9, Hongjing Xinhuiyuan, Qingpu District, Shanghai
gcfai@dongfangyuzhe.com


WeChat official account
friend link



13004184443
立即获取方案或咨询
top