Home > Information > News
#News ·2025-01-06
This article is reproduced by the authorization of the 3D Vision Heart public number, please contact the source.
Thesis title: PC-BEV: An Efficient Polar-Cartesian BEV Fusion Framework for LiDAR Semantic Segmentation
Authors: Shoumeng Qiu, Xinrun Li, Xiangyang Xue, Jian Pu
Address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.14821
Lidar point cloud segmentation is the core task in the field of autonomous driving, whose goal is to accurately understand the semantic information of the surrounding environment. At present, the methods in this field are mainly divided into three categories: point-based methods, voxel-based methods and projector-based methods.
Among them, projection-based methods are favored because of their ability to efficiently process projection point clouds using 2D convolutional neural networks (CNNS). However, compared with voxel-based methods with a large amount of computation, the inevitable loss of information in the projection process from 3D to 2D limits the performance of this algorithm.
In order to narrow this performance gap, multi-view fusion technology emerged by integrating complementary information captured by different projection techniques. Recent multi-view fusion methods, such as AMVNet, GFNet, and CPGNet, enhance presentation learning through point-based feature interactions.
However, due to the lack of fixed correspondence between views, these methods require costly grid sampling and scattering operations, which affect real-time performance. In addition, feature fusion is usually limited to the region where the point exists and may ignore valuable contextual information in the surrounding region.
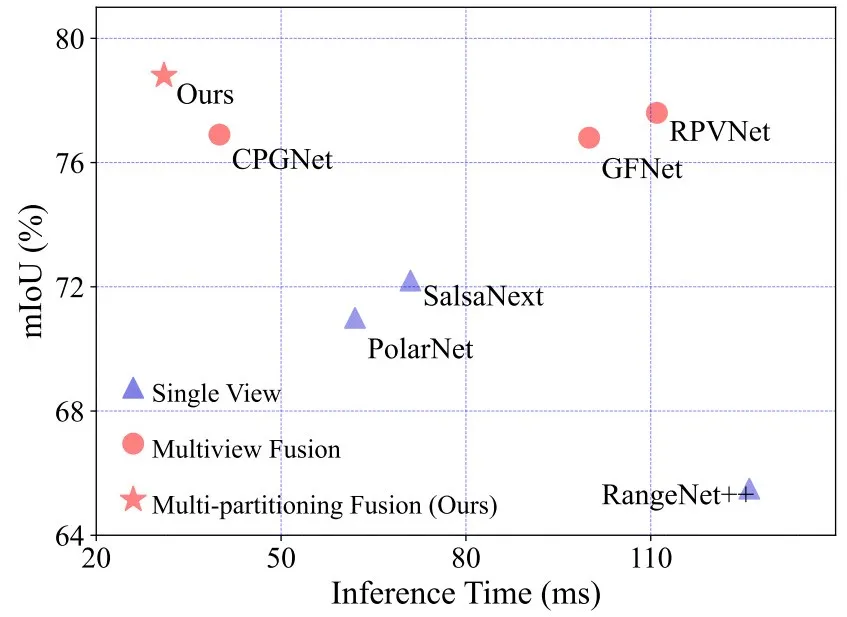
Compared with other projection-based methods, the results show the advantages of the proposed method in terms of performance and speed. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
To overcome these limitations, the authors propose an innovative multi-partition feature fusion framework that operates entirely within the BEV space, taking full advantage of the fixed correspondence between polar coordinates and Cartesian partitioning schemes. This method is inspired by the similarity between polar coordinate partitioning in BEV and spherical coordinate partitioning in range view, and experiments show that the performance of different partitioning methods is complementary.
In order to promote feature fusion between polar coordinates and Cartesian branches, an efficient and effective fusion method based on remapping is introduced. Based on the inherent fixed coordinate correspondence between polar coordinates and Cartesian space partitions in the same BEV space, the corresponding parameters are calculated in advance, and then efficient feature fusion is realized by carefully designed remapping operation. This method is 170 times faster than previous point-based feature interaction methods. In addition, all feature fusions operate at BEV spatial locations, which not only achieves dense fusion, but also preserves more valuable contextual information than previous point-based approaches.
The authors also propose a hybrid Transformer-CNN architecture for BEV feature extraction. Self-attention in the Transformer block captures global scene information, followed by a lightweight U-net style CNN for detailed feature extraction. The experimental results show that this architecture enhances the model performance while maintaining the real-time inference capability.
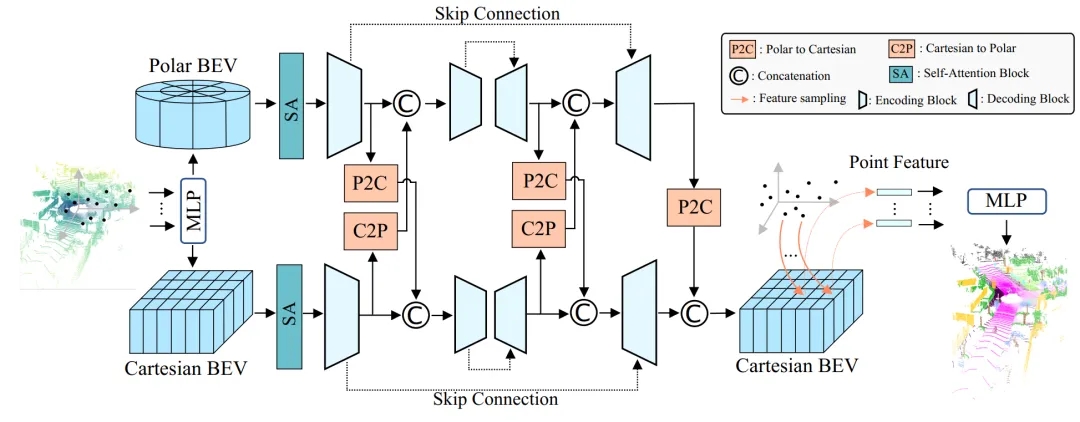
Figure 2 | Flowchart of the polar-Cartesian BEV fusion framework for 3D point cloud semantic segmentation task. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile


For the final semantic prediction, since the goal of this method is to provide semantic prediction for each point in the scene, it is necessary to obtain the features of each point used for category prediction in the projection space. For features extracted from different branches, a common practice in previous methods is to retrieve the corresponding features for each point through a grid sampling (GS) operation. The features sampled from different branches are then fused. Finally, the fused features are used to obtain the final semantic prediction results. The previous point-based output fusion can be expressed as (here the author assumes fusion using join operations) :
To further speed up model reasoning, the authors use a remapping operation to align the features of one branch with those of another, which enables the model to perform grid sampling on the remapping branch only once. In the paper, the authors chose to align the features extracted from the polar coordinate branch with Cartesian space because the authors experimentally found that this performed slightly better than the opposite way. The authors connect the remapped polar coordinate features with Cartesian features, and then use grid sampling to obtain the BEV position features for each point. Therefore, the final point-level feature output in the author's method can be expressed as:

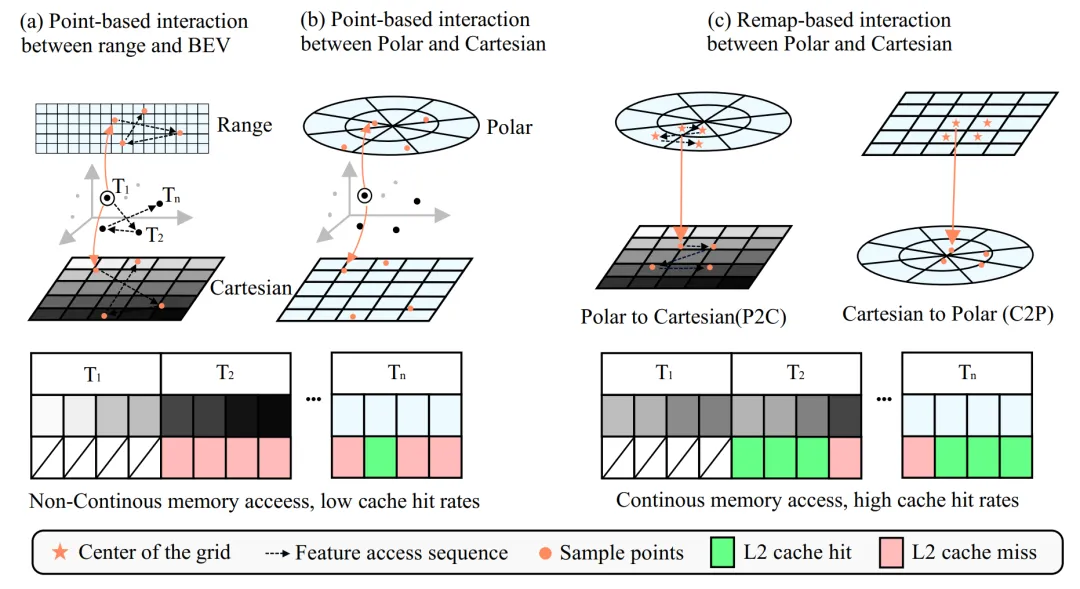
Figure 3 | Compare the feature interactions between the previous point-based approach and the remap-based approach in different Settings. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
Unlike previous multi-view fusion methods, which operate in different projection Spaces, the dynamic grid-to-grid correspondence is different due to information loss in the projection process. The proposed method benefits from the fixed position correspondence of two partition branches in the same BEV space, which provides an opportunity to improve the efficiency of the feature fusion process.
Specifically, the authors employ remapping techniques to align features under two different partitioning methods. Since the grid correspondence between the two branches is fixed, the remapping parameters can be calculated in advance to achieve efficient feature fusion. The authors provide detailed steps for remapping operations, highlighting the advantages of remap-based interactions over point-based interactions. Taking the remapping process from polar space to Cartesian space as an example, note that the remapping from Descartes to polar space follows the same principle.

So far, the coordinate correspondence between Cartesian and polar coordinate branches has been established, which is fixed so that fusion can be calculated in advance. The center of the grid can be regarded as a point, and the previous point-based method can be used for feature fusion. However, the authors' experiments show that this approach is inefficient in practice.
In order to perform feature fusion more efficiently and effectively, we develop a feature fusion operation based on remapping, which significantly improves the speed of feature alignment between two branches. Traditional point-based methods are slow mainly because of grid sampling operations and scattering back operations. They treat each point individually as point-level parallel processing, resulting in a high cache miss ratio in the experiment.
Unlike the point-based approach, the authors' remap-based operation takes into account the continuity of spatial locations, making the process more memory accessible and significantly speeding up the computation. Figure 3 compares different feature fusion methods. It is important to note that not every grid in one branch has a corresponding area in another branch, due to changes in space occupancy patterns.
If a spatial location in one branch is not available in another branch, zero fill is simply applied to that location. A more detailed efficiency analysis can be found in the supplementary materials. Remap-based fusion methods provide additional advantages by incorporating more contextual information into the fusion process.
As shown in Figure 4, the point-based method fuses only in the region where there are points, discarding features without points, which is called sparse fusion by the author. In contrast, the remap-based approach makes fusion possible in the entire BEV space, achieving dense fusion and enriching the feature information from another branch.
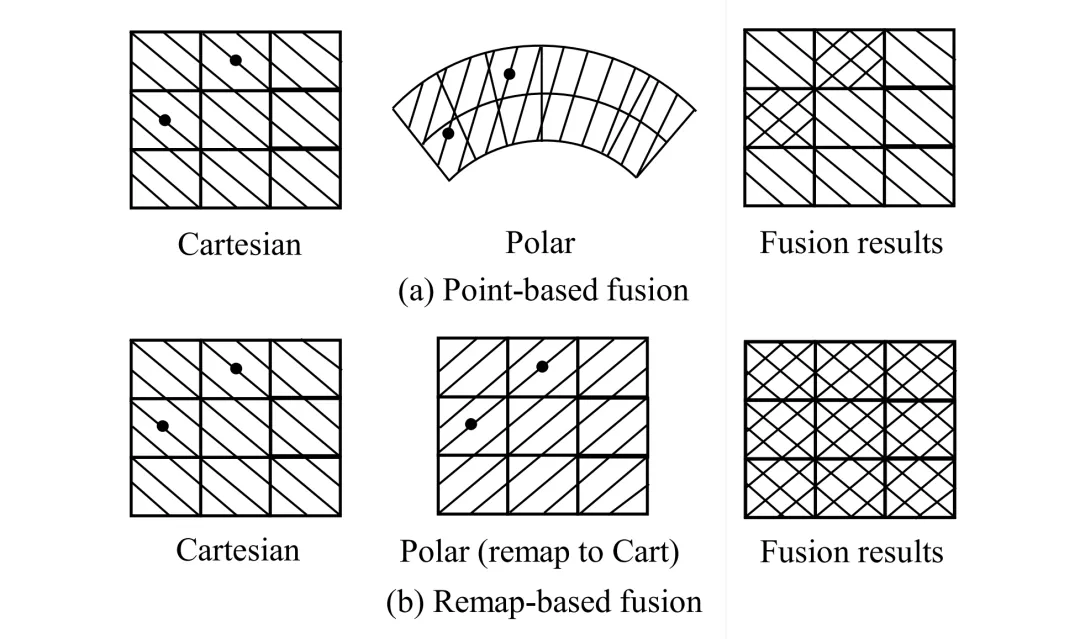
Figure 4 | Comparison between the results of point-based interactions and the results of remap-based interactions. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
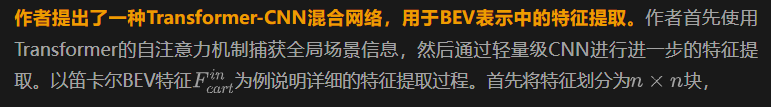
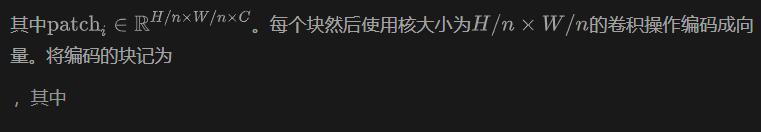
Since the attention mechanism lacks the ability to distinguish position information in the input sequence, the authors introduce sinusoidal position coding PE into the feature. The final block-embedded input self-attention can be expressed as:


Features rich in global information are then fed into an efficient CNN model for further extraction. The author uses a U-net architecture for CNN. Experiments show that the Transformer-CNN hybrid architecture in this paper offers advantages in both performance and reasoning speed.
The authors conducted extensive experiments on the SemanticKITTI and nuScenes datasets, demonstrating that this approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with faster inference speeds.
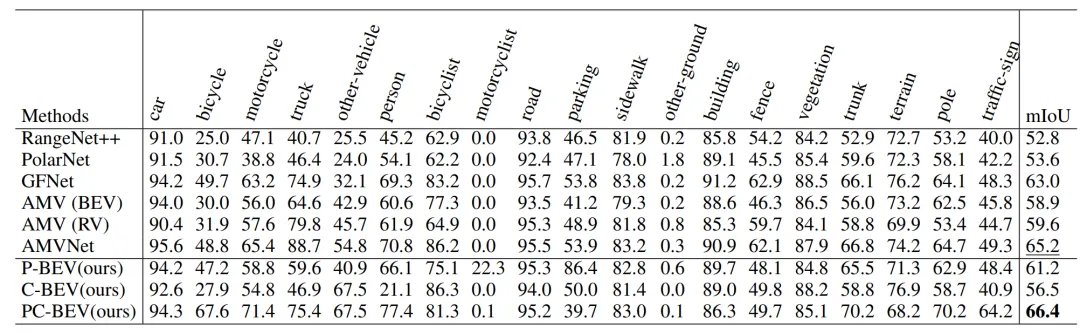
Table 1 | Quantitative comparison in the SemanticKITTI test set. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
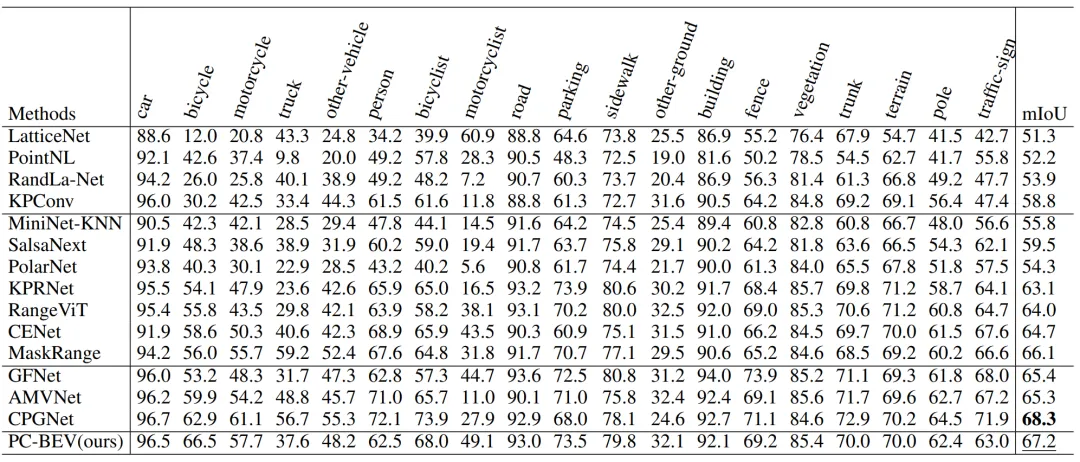
▲ Table 2 | Quantitative comparison of the SemanticKITTI validation machines. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
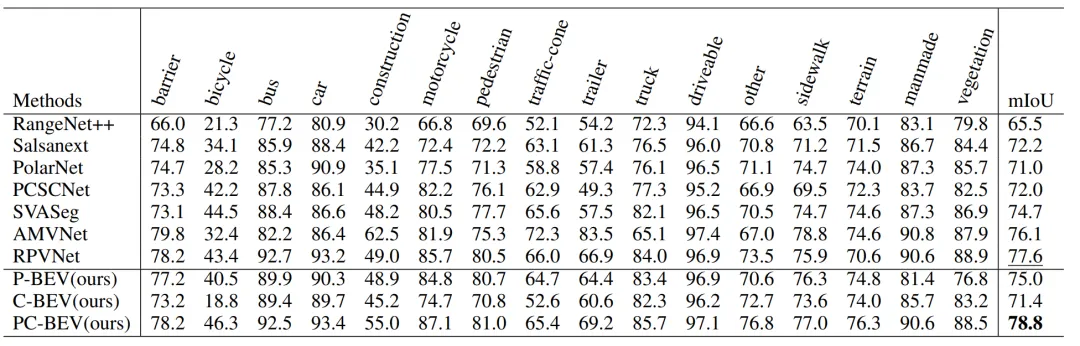
Table 3 | Quantitative comparison in nuScenes test sets. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
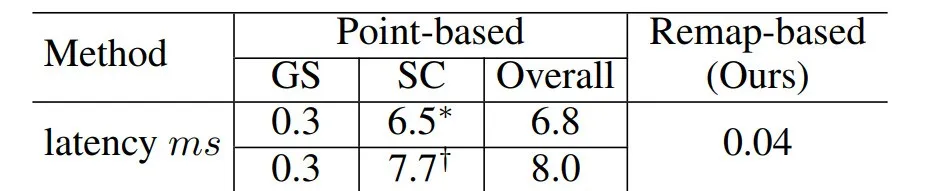
▲ Table 4 | Comparison of interaction efficiency based on remapping. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
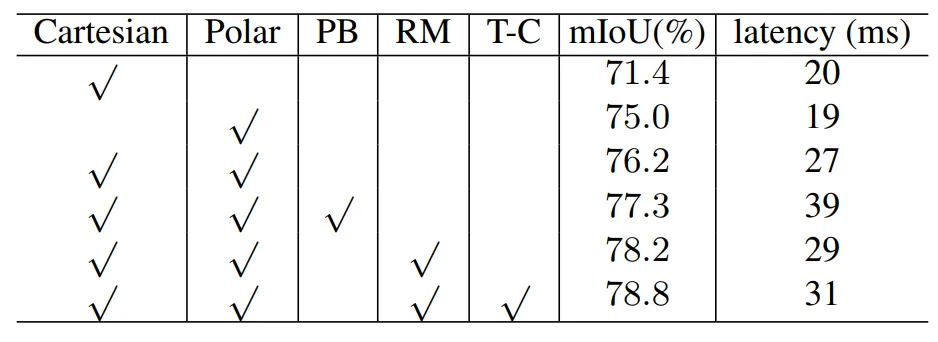
Table 5 | Ablation studies on the nuScenes validation set. ©️【 Deep blue AI】 Compile
A novel real-time liDAR point cloud segmentation method is presented in this paper. By using the efficient remapping spatial alignment fusion strategy developed by the author, this technique not only greatly improves the processing speed, but also exceeds the performance of traditional point-based interaction methods, while retaining more detailed context information.
In addition, the article introduces a hybrid Transformer-CNN architecture that further enhances the overall performance of the model while maintaining real-time processing capabilities. Extensive experiments on SemanticKITTI and nuScenes datasets fully demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method.
Going forward, the researchers could further explore the application of this technique to BEV (bird's eye view) representations generated from multi-camera image data to expand its range of applications.

2025-02-17

2025-02-14

2025-02-13
13004184443
Room 607, 6th Floor, Building 9, Hongjing Xinhuiyuan, Qingpu District, Shanghai
gcfai@dongfangyuzhe.com


WeChat official account
friend link



13004184443
立即获取方案或咨询
top